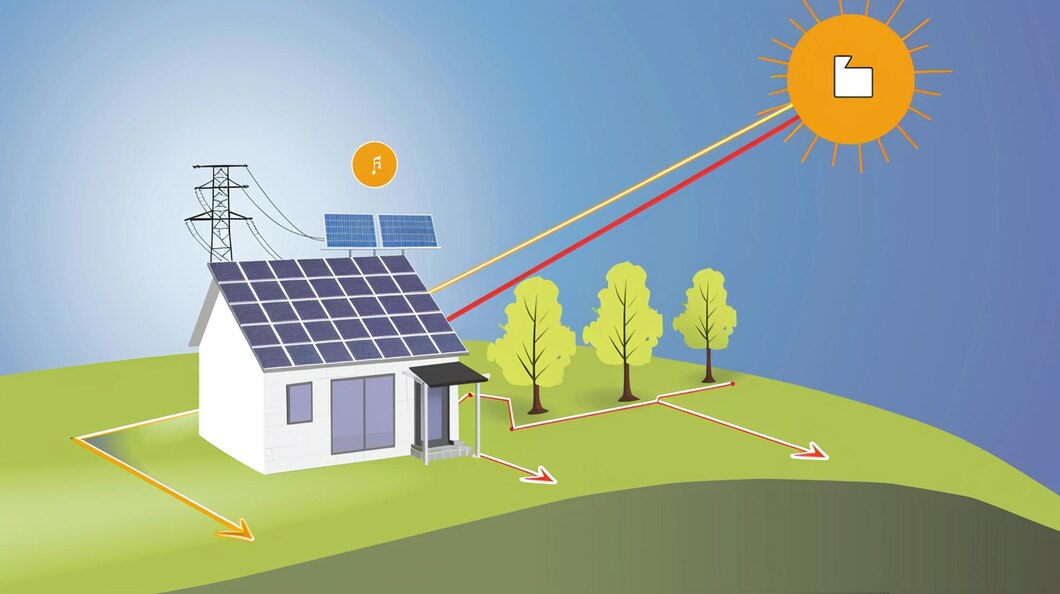
Off- Grid Solar System
An Off-Grid Solar System is a renewable energy solution designed to operate independently of the local utility grid. It provides complete energy self-sufficiency by generating, storing, and supplying electricity on-site. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations without grid access or for users seeking full energy independence. They are typically equipped with battery storage to ensure a reliable power supply even during periods of low solar generation.
How Off-Grid Solar Systems Work
Solar Energy Generation:
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
Battery Storage:
The generated DC electricity charges a battery storage system, which stores energy for use during cloudy days, nighttime, or periods of high demand.
Inverter Conversion:
An inverter converts DC electricity from the panels or batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which powers appliances and equipment.
Energy Management:
A charge controller manages the flow of electricity, preventing overcharging or deep discharging of the batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Key Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
Solar Panels:
Photovoltaic (PV) panels generate electricity from sunlight and are the primary energy source.
Battery Bank:
Batteries store excess electricity generated during the day for use at night or during low sunlight periods. Lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries are commonly used in off-grid systems.
Inverter:
The inverter converts stored or directly generated DC electricity into AC electricity, compatible with standard appliances.
Charge Controller:
This device regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
Mounting Structures:
Panels are mounted securely on rooftops or ground-based structures, oriented to maximize sunlight exposure.
Wiring and Electrical Components:
High-quality cables, switches, and connectors ensure safe and efficient operation.
Benefits of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Energy Independence:
Off-grid systems provide complete autonomy from the utility grid, ensuring a reliable power supply regardless of external conditions.
Remote Access:
They are ideal for areas without grid access, such as remote villages, farms, or cabins.
No Grid Dependency:
Off-grid systems continue to operate during grid outages, offering uninterrupted power.
Environmental Benefits:
Using renewable solar energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
Customizable Design:
Off-grid systems can be tailored to specific energy needs and scaled as required.
Limitations of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Higher Upfront Costs:
Off-grid systems require batteries and additional components, making them more expensive than grid-tied systems.
Maintenance Requirements:
Battery systems need regular maintenance and eventual replacement, increasing long-term costs.
Energy Storage Dependency:
System performance relies heavily on battery capacity, which may be limited during prolonged periods of low sunlight.
Over- or Under-Sizing Risks:
Improper system sizing can lead to insufficient power supply or wasted energy, requiring careful planning and expert design.
Applications of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Remote Locations:
Farms, rural homes, and remote businesses without grid access benefit significantly from off-grid systems.
Disaster-Prone Areas:
Off-grid systems provide reliable energy during natural disasters, where grid power may be unavailable.
Standalone Infrastructure:
Used for powering telecommunication towers, water pumps, or lighting systems in isolated areas.
Sustainable Living:
Ideal for individuals or communities committed to energy independence and self-sufficient living.
Factors to Consider Before Installing an Off-Grid Solar System
Energy Requirements:
A thorough analysis of energy needs helps determine the system’s size and battery capacity.
Battery Storage Capacity:
Batteries should be sized to store enough energy for nighttime use and periods of low sunlight.
Location and Solar Potential:
The site’s sunlight availability impacts the system’s efficiency and design.
Upfront and Maintenance Costs:
Budget considerations must include the initial investment and long-term maintenance costs, such as battery replacement.
Backup Solutions:
A backup generator or additional energy sources may be necessary to supplement power during extended periods of low solar generation.
Conclusion
Off-grid solar systems provide a reliable, sustainable, and independent energy solution for areas without grid access or for users seeking complete autonomy. While they require a higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance, the benefits of energy independence and environmental sustainability make them an excellent choice for specific applications. By carefully designing and implementing the system, users can achieve long-term energy security and contribute to a cleaner, greener future.